Packing line design is critical to modern manufacturing and logistics, ensuring products are efficiently and effectively prepared for distribution. A well-designed packing line can significantly enhance productivity, reduce costs, and improve product quality. This article explores the key elements of packing line design, including layout, equipment, automation, and sustainability, providing a comprehensive understanding of this essential process. We will also discuss how packing line design applies to various industries handling granules, liquids, and powders, and how it can be adapted for bagged, boxed, and bottled packaging.
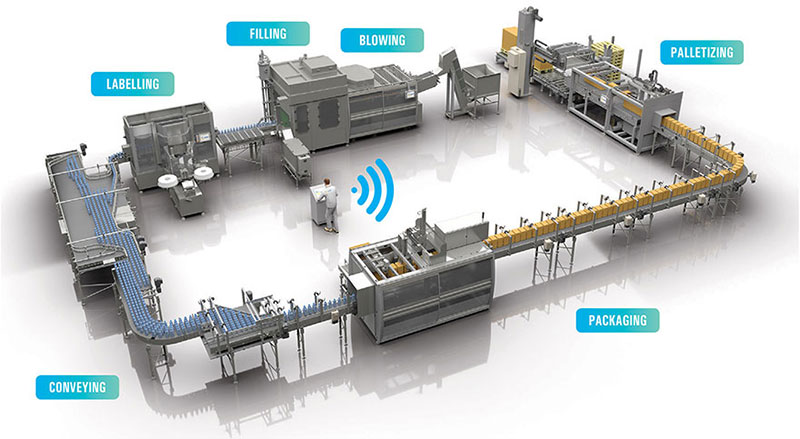
Understanding Packing Line Design
Packing line design involves systematically arranging equipment and processes to package products efficiently. The primary goal is to optimize the flow of products from the production line to the final packaging stage, ensuring minimal waste, maximum speed, and high quality. Key considerations include the type of products being packaged, the packaging materials, and the required throughput.
Key Components of Packing Line Design
1. Layout: The layout of a packing line is crucial for efficiency. It should minimize the distance products travel and reduce bottlenecks. Common layouts include straight, U-shaped, and L-shaped configurations, each with its advantages depending on the available space and specific requirements.
2. Conveyors: Conveyors are the backbone of any packing line, transporting products between different stages. Various types of conveyors, such as belts, roller, and chain conveyors, are used depending on the product type and packaging requirements.
3. Packaging Machines: These machines perform specific tasks such as filling, sealing, labeling, and wrapping. The choice of machinery depends on the product type and the desired packaging. For example, liquid products require filling machines, while solid products may need wrapping or sealing machines.
4. Quality Control: Ensuring product quality is paramount. Quality control stations equipped with sensors and cameras can detect defects and ensure that only products meeting the required standards proceed to the next stage.
5. Automation: Automation plays a significant role in modern packing lines, increasing efficiency and reducing human error. Automated systems can handle repetitive tasks, such as sorting, packing, and palletizing, freeing up human workers for more complex tasks.
Applications in Different Industries
Packing line design is versatile and can be tailored to various industries, including those handling granules, liquids, and powders. Below are examples of how these designs are adapted for different packaging formats:
1. Granules:
- Industry: Food and Beverage (e.g., coffee beans, rice), Agriculture (e.g., seeds, fertilizers).
- Packaging: Bagged, Boxed.
- Example: A coffee packaging line might include bulk hoppers feeding into precise weighing and bagging machines, followed by heat sealing and labeling.

2. Liquids:
- Industry: Pharmaceuticals (e.g., syrups), Chemicals (e.g., cleaning agents), Food and Beverage (e.g., juices, sauces).
- Packaging: Bottled.
- Example: A juice packing line would use high-speed filling machines to fill bottles, capping machines to secure them, and labeling machines to apply product labels. Automated inspection systems would ensure quality control.

3. Powders:
- Industry: Pharmaceuticals (e.g., powdered medicines), Food (e.g., flour, spices), Chemicals (e.g., detergents).
- Packaging: Bagged, Boxed.
- Example: A flour packing line might involve bulk storage silos feeding into filling machines, which dispense precise amounts into bags. The bags are then sealed, labeled, and boxed for distribution.
Designing an Efficient Packing Line
1. Assessing Requirements: The first step in packing line design is to assess the specific needs of the operation. This includes understanding the types of products, packaging materials, and production volumes. Detailed analysis helps in selecting the right equipment and layout.
2. Equipment Selection: Choosing the right equipment is critical. Factors to consider include the speed of operation, compatibility with different product sizes, and ease of maintenance. Investing in high-quality, versatile machines can lead to long-term savings.
3. Layout Planning: Efficient layout planning involves creating a logical flow of products. Using software tools for simulation can help in visualizing different layouts and identifying potential bottlenecks. The goal is to create a streamlined process that minimizes handling and maximizes throughput.
4. Integration of Automation: Automation can significantly enhance packing line efficiency. Integrating automated systems such as robotic arms for palletizing, automated guided vehicles (AG
Vs) for material transport, and sensors for quality control can lead to substantial improvements in productivity and accuracy.
5. Sustainability Considerations: Modern packing line design also incorporates sustainability practices. This includes using eco-friendly packaging materials, reducing energy consumption through efficient machinery, and minimizing waste through precise control systems.
Case Study: Landpack Packaging Machine
Landpack Packaging Machine is a leading manufacturer of packing lines, specializing in solutions for a variety of products including granules, liquids, and powders. Their innovative designs cater to different packaging formats such as bags, boxes, and bottles, ensuring high efficiency and quality.

Consider a company manufacturing various products, such as granules, liquids, and powders. Landpack's packing line design for such a company would involve several stages and various packaging formats:
1. Granules:
- Filling Machines: Bulk hoppers and precision scales ensure accurate filling into bags or boxes.
- Sealing and Labeling: Heat sealers for bags and automated labeling systems ensure consistency.
- Conveyors: Custom-designed to handle the movement of bagged or boxed products efficiently.
2. Liquids:
- Filling Machines: High-speed fillers that can handle different bottle sizes and viscosities.
- Capping and Labeling: Automated capping machines and label applicators integrated with quality control systems.
- Conveyors: Designed to minimize spillage and ensure smooth transitions between stages.
3. Powders:
- Filling Machines: Auger or vacuum fillers for precise measurement and filling.
- Sealing and Labeling: Machines that handle the unique sealing requirements of powder products and apply labels accurately.
- Conveyors: Configured to handle the specific needs of powder transport and packaging.
Challenges in Packing Line Design
Despite the numerous benefits, packing line design can pose several challenges:
1. Customization: Each product may require specific packaging solutions, leading to complex and customized packing lines. Balancing customization with standardization is a key challenge.
2. Integration: Integrating different machines and systems can be complex. Ensuring seamless communication and coordination between various components is crucial for a smooth operation.
3. Maintenance: Regular maintenance is essential to prevent breakdowns and ensure consistent performance. Designing packing lines with easy access to critical components can simplify maintenance.
4. Cost: Initial investment in high-quality equipment and automation can be high. However, this is often offset by long-term savings in labor and increased efficiency.
Future Trends in Packing Line Design
The future of packing line design is likely to be shaped by several emerging trends:
1. Advanced Automation: Continued advancements in robotics and AI will lead to even more sophisticated automation, capable of handling complex tasks with greater precision and flexibility.
2. IoT Integration: The Internet of Things (IoT) will enable real-time monitoring and control of packing lines, allowing for predictive maintenance and increased efficiency.
3. Sustainable Practices: Growing environmental awareness will drive the adoption of sustainable practices, such as biodegradable packaging materials and energy-efficient machinery.
4. Customization and Flexibility: As consumer demand for personalized products increases, packing lines will need to become more flexible, and capable of quickly adapting to different packaging requirements.
Conclusion
Packing line design is a complex but essential aspect of modern manufacturing and logistics. By carefully considering factors such as layout, equipment, automation, and sustainability, companies can create efficient packing lines that enhance productivity, reduce costs, and ensure high product quality. Whether dealing with granules, liquids, or powders, and regardless of the packaging format—be it bags, boxes, or bottles—an optimized packing line is crucial for meeting the demands of today's competitive market. As technology continues to evolve, the future promises even more innovative solutions to meet the growing demands of the market. Landpack Packaging Machine, with its cutting-edge designs and versatile solutions, stands at the forefront of this industry, ready to meet these challenges and drive future advancements.